Short Strangle
All Option Strategies
Short strangle options trading strategy is an excellent strategy to be deployed when the investor is expecting little to no volatility in the market. In spite of no price movements, the investor can make profits using the short strangle.
Short strangle is formed by writing one slightly out-of-the-money put option and writing a slightly out-of-the-money call option, both for the same underlying asset and with the same options expiration date.
Short strangle differs from a short straddle in the way that the strike prices for both the options are different in short strangle. Also, do not confuse this strategy with Short Put either as a lot of beginner level traders end up doing.
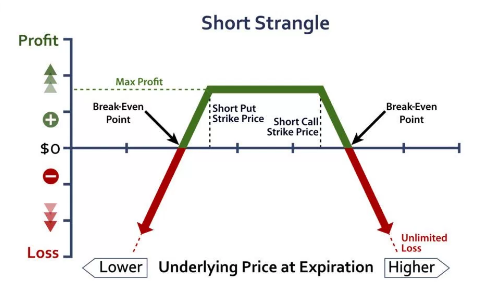
The strike price of the put option is less than the current price and that of the call option is higher than the current stock price.
The short strangle strategy has limited profit potential, wherein the profit will be received only when the prices remain between the two strike prices and it is limited to the sum of the two premiums received.
However, the risk potential of the strategy is unlimited.
As soon as the price of the underlying moves beyond the strike price range, the trader will incur losses. The losses are big enough to be compensated by the premiums received.
Short strangle is a net credit strategy and is also known as a credit spread, because of the premiums received right at the entry.
Short Strangle Timing
The ideal time to use a short strangle is when the trader is expecting that there will be little or no movement in the price of the underlying asset. In this case, the trader will write an OTM put option at a strike price lower than the current price, and will write an OTM call option at a strike price higher than the current price.
Premiums are received for writing both the options. The intention of the trader is that the stock price remains between the two option strike prices and the options expire worthlessly.
The short strangle strategy can also be used when the implied volatility of the stocks is very high and the options seem to be overvalued. The short strangle can be formed and positions can be closed before expiry to gain profit from the price correction.
Compared to the short straddle, the premiums received for short strangle are less. The out-of-the-money options generate less premium than the at-the-money options. However, due to a range between the strike prices, the price swing has to be big enough to lead to losses.
The short strangle strategy is a limited reward and unlimited risk strategy. The profit potential of the strategy is limited to the sum of the two premiums received on the options. The ideal situation for maximum profit is when the price remains between the two strike prices and there is not much volatility.
Both the options will expire worthless and premiums will be received, in spite of no price movement.
The maximum loss can be unlimited because the price can go up or down to any extent in either direction. If the price goes above the call strike price, the put option will expire worthlessly and the premium will be received, but the call option will be exercised and result in a loss.
Similarly, if the price goes below the put strike price, the call option will expire worthlessly and the premium will be received, but the put option will be exercised and result in a loss.
Short Strangle Example
In the same scenario as for long strangle, where NIFTY is at 7900 points and the trader is now expecting that there will be no movement in the price. He will then set up a short strangle.
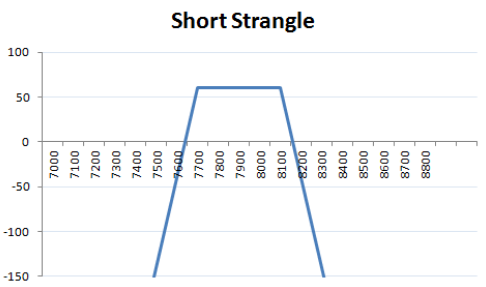
The trader writes a put option at 7700, paying a premium of ₹28 and writes a call option for 8100, paying a premium of ₹32. Both the options are out-of-the-money.
Scenario 1:
If NIFTY closes at 7800, it remains within the range of the strike prices of the two options. Therefore, both the call and put options will expire worthlessly and the premiums will be received.
The net profit will be 28+32= ₹60.
This is the maximum profit that can be generated using short strangle.
If short straddle was used, instead of short strangle, at 7800 the trader would have incurred a loss. Short strangle allows for a wider range of price movement to keep giving profits. However, the profit received in short strangle is less than the short straddle.
Scenario 2:
If NIFTY closes at 7400, it implies high volatility and the trader will incur a loss. The call option will expire worthlessly and a premium of Rs 32 will be received.
The put option will be exercised and the loss will be equal to (7700-7400)= ₹300.
The net loss will be 300-28= ₹272.
The net payoff of the strategy will be -272+32= – ₹240, i.e. loss of Rs 240.
The loss will keep on increasing as the price of the underlying keeps moving away from the current price. This indicates that short strangle is not suitable for markets with high volatility.
Scenario 3:
If NIFTY closes at 8160, the put option will expire worthlessly and a net income of Rs 28 will be received. The call option will be exercised and the loss will be equal to 8160-8100= ₹60.
The net loss will be 60-32= ₹28.
The net payoff of the strategy will be 28-28= ₹0.
This is the upper breakeven point, wherein the loss incurred due to the exercise of the call option is compensated by the premium received due to the put option expiring worthless.
Short Strangle Advantages
- This strategy has more range for earning profits compared to short straddle. The price of the underlying can be within the range of the two strike prices to make profits.
Short Strangle Disadvantages
- The premiums received are less, compared to short straddle.
- The risk associated with the strategy is unlimited.
- The profit is limited, with a maximum cap of the sum of the two premiums received.
Short Strangle in a Nutshell
As a bottom line, short strangle is a strategy to be used only at the time when the trader is surely convinced of low or no volatility in the market.
If the stock market prediction does not come out true, the strategy can cause unlimited loss.
However, compared to the short straddle, short strangle is less risky as the price can move within a range. The payout is also less than a short straddle.
In case you are looking to get started with options trading or share market investments in general, we will assist you in taking steps ahead.
More on Share Market Education:









