NSE Nifty
More On Share Market
NSE Nifty is one of the most common terms you might have heard in the stock market circuit. If you are a beginner, you might be getting overwhelmed by this crusade of abbreviations and this NSE Nifty be one of those.
However, don’t worry! In this quick review, we will talk about what exactly this ‘exchange’ does and how is it used practically in a trader’s life.
Also Read: Nifty and Sensex
But wait! What is this ‘exchange’ thing now?
Well, a stock exchange is a platform where securities are traded between buyers and sellers. In India, The National Stock Exchange or NSE is the leading stock exchange in India.
NSE Nifty Meaning
Want to know How many Stock Exchanges in India? NSE Nifty is one of the stock exchanges. Let’s discuss it in detail here.
NSE Nifty is one of the largest stock exchanges in the world in terms of equity trading volume and the largest stock exchange in India in terms of total and average daily turnover for equity shares every year since 1995.
Approximately 1600 companies are listed on the NSE.
Also Read: What is BSE & Sensex?
Some quick facts about NSE:
- It started operating in the year 1994.
- It launched electronic screen-based trading in 1994.
- NSE was the first stock exchange in India to launch derivatives trading and trading through the internet in the year 2000.
To get into a trade with NSE, learn how to open NSE account?
Before introducing the term “Nifty“, let us try to understand the meaning of the stock market index.
If someone asks how the stock market is doing, you cannot answer the question by thinking about all the hundreds of companies listed on the exchange and then, there are so many stock market types too.
You will naturally choose some financially sound companies from every sector which may be considered as representatives of their respective sectors to give a whole and accurate picture of the market.
A stock market index does the exact same thing.
NIFTY50 is the index for measuring the performance of stocks listed on the National Stock Exchange. As the name suggests, the Nifty 50 companies list comprises of 50 companies selected from a total of 13 sectors. As the values of the stocks within the index change, the value of the index also changes correspondingly.
There can be any number of different indices for a stock exchange.
The difference may be on the basis of market cap (small-cap index, mid-cap index or large-cap index).
Some quick facts about NIFTY50:
- NIFTY 50 is owned and managed by India Index Services and Products Ltd. (IISL). The governance structure comprises of the Board of Directors, the Index Policy Committee and the Index Maintenance Sub-Committee
- Its base period is November 3, 1995, which marks the completion of one year of operations of NSE’s Capital Market Segment.
- Its base value has been set at 1000, and a base capital of Rs 2.06 trillion.
- The index is rebalanced on a semi-annual basis. The pre-decided dates for this purpose are January 31 and July 31 of every year
- As of March 30, 2017, it represents about 62.9% of the free-float market capitalization of the stocks listed on NSE.
NSE Nifty Option Chain
Nifty option chain lists out all the stocks that have the options trading facility available with all sorts of details out. These details include:
- Puts
- Calls
- Strike Price
- Bid Quantity
- Underlying Asset Price
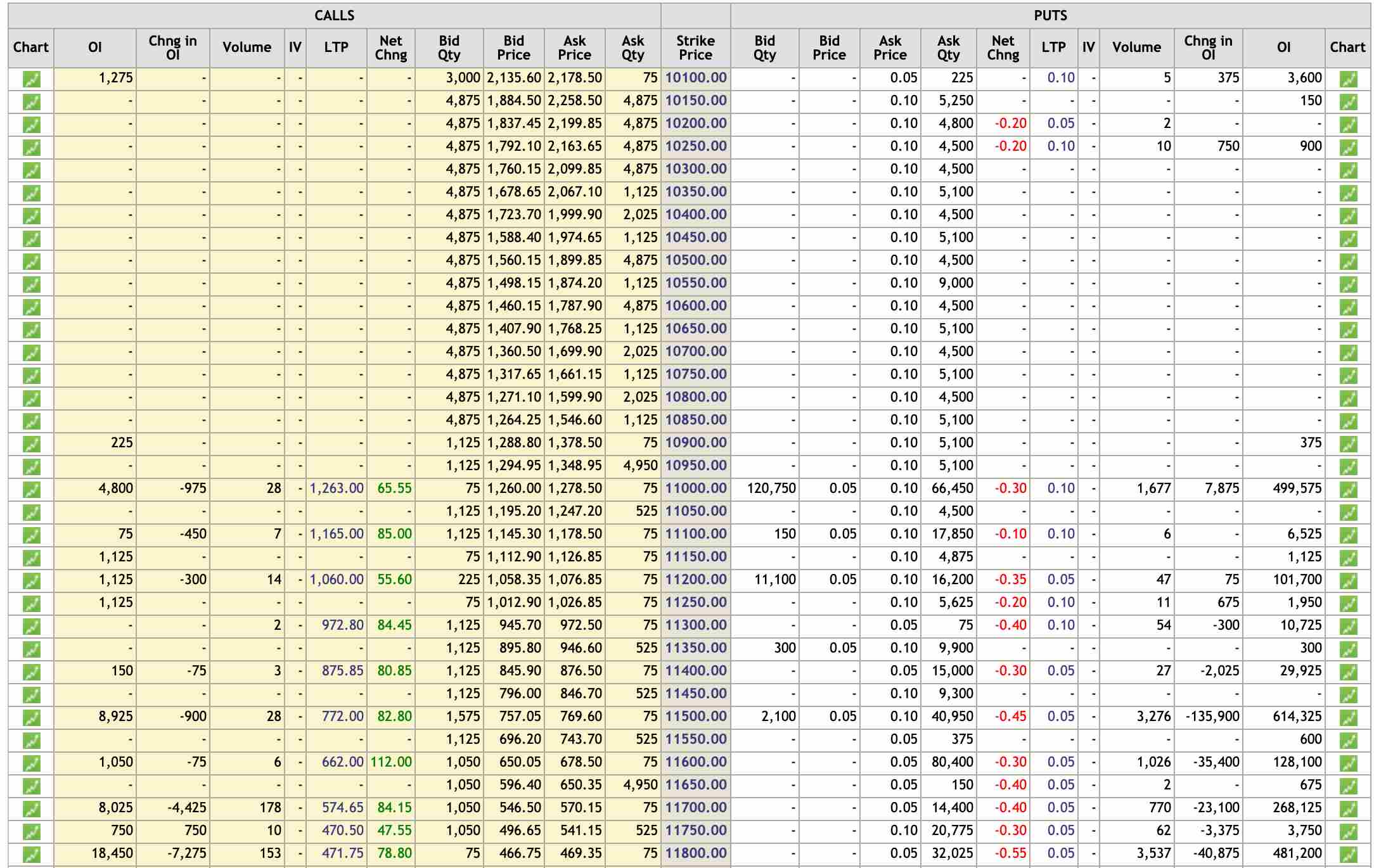
For instance, here is a quick glimpse of how an NSE Nifty Option chain looks like:
If you look closely at the option chain above, you will find all the relevant data you may need before going ahead with any put or call option contract with any seller or buyer out there.
Each column has its own relevance as discussed below:
- LTP is the last traded price of the underlying asset in question. If the market is closed for the day, the LTP becomes the closing price of that security for that day.
- A few columns talk about the change in the respective metric. That change is the positive or negative movement in the value of the specific metric for the put or call option.
- The strike price is the price that is finalized between the parties at the onset of the contract.
Furthermore, there are a lot of insights one can take just by giving a quick glimpse at the options chain. For instance:
- As shown in the above representation, the yellow shaded cells imply in-the-money options (ITM) and the cells that have no shading imply out-of-money options (OTM).
- Although, we are currently talking about the options chain in the context of NSE Nifty, however, similar chains can also be seen for other indices and even stocks that have options trading enabled.
Calculation Methodology of NSE Nifty50
The NIFTY 50 is computed using the free-float market capitalisation weighted method.
It means that a company’s free-float capitalization is considered while calculation of the index and assigning weights to stocks in the index. Free-float refers to those shares of the company that are readily available for trading in the market.
The following categories are excluded from the free float factor computation:
- Promoter and promoter group holdings
- Government holding in the capacity of the strategic investor
- Shares held by promoters through ADR/GDR
- Strategic stakes by corporate bodies
- Foreign Direct Investments (FDIs)
- Equity held by associate/group companies (cross-holdings)
- Employee Welfare Trusts
- Shares under lock-in category
NSE Nifty Price Index Calculations:
Firstly, let us understand the term “Investible Weight Factors”.
Investible Weight Factors or IWF is a unit of floating stock expressed in terms of a number available for trading and which is not held by any of the above-mentioned categories. IWF is calculated for each company based on the public shareholding of the companies as disclosed in the shareholding pattern submitted to the stock exchanges quarterly.
For example, a company called ABC has a total of 1,00,000 shares. The other shareholding pattern is:
| Business Entity | Shares | Share %age |
| Promoter and promoter group holding | 19,75,000 | 19.75% |
| Government Holding | 50,000 | 0.5% |
| Holdings of promoters through ADR/GDR | 2,50,000 | 2.5% |
| Cross Holdings | 12,575 | 0.13% |
| Employee Welfare Trusts | 1,45,987 | 1.46% |
| Locked-in shares | 14,78,500 | 14.79% |
In this case, IWF will be calculated as follows:
IWF = [1,00,00,000 – (19,75,000 + 50,000 + 2,50,000 + 12,575 + 1,45,987 + 14,78,500)] / 1,00,00,000 = 0.61
The level of NIFTY50 Index reflects the total market value of all the stocks in the Index relative to the base period November 3, 1995. The total market capitalisation is the product of market price and the total number of outstanding shares of the company.
Market Capitalization = Shares outstanding * Price
Free Float Market Capitalization = Shares outstanding * Price * IWF
Index Value = Current Market Value / Base Market Capital * Base Index Value (1000)
Base market capital of the Index is the aggregate market capitalisation of each scrip in the Index during the base period. The market cap during the base period is equated to an Index value of 1000, also known as the base Index value.
How To Select Nifty50 Stocks?
Let’s have a look at some of the top factors on how these 50 stocks are selected to be part of the NSE Nifty index:
Liquidity:
Market impact cost is a term that is the best measure of the liquidity of a stock. It reflects the costs incurred when trading an index. To be a part of the NIFTY 50, a stock should have an average impact cost of 0.50% or less during the last six months for 90% of the observations, for the basket size of Rs. 100 million.
Listing History:
The NSE listed company should have a minimum listing history of 6 months.
Futures and Options (F&O) Category:
Companies that are allowed to trade in the F&O segment are only eligible to be a part of NIFTY 50.
Also, if a company that has just launched its IPO fulfils the normal eligibility criteria for NIFTY for a period of three months can also be a part of the index.
Once you are aware of NSE, know about the difference between BSE and NSE
NSE Nifty50 Stocks Weightage
The top 10 NIFTY50 companies along with their weightages are as follows:
Company Name Weightage HDFC Bank 9.42% Reliance Industries 7.86% Housing Development Finance 7.46% ITC 5.68% Infosys 5.39% ICICI Bank 4.32% Tata Consultancy 4.16% Larsen & Toubro 4.09% Kotak Mahindra Bank 3.82% Maruti Suzuki 2.77%
There is clear segregation based on the industries the above-listed companies come from. For instance, 3 out of the top 10 listed companies come from the banking sector while Infosys, TCS belonging to the IT sector take away almost 10% of the overall market cap.
With this, we’d like to wrap up this piece on NSE Nifty. Feel free to share your thoughts in the comments section below.
In case you are looking to get started with share market trading or want to open a demat or trading account – just fill in some basic details in the form below.
A callback will be arranged for you:
More on Share Market Education:
If you wish to learn more about the share market, here are a few references for you:










mirzaakbarbaig9700@gmail.com
Hi sir interested in stock market investment and trading Nifty 50