Long Call
All Option Strategies
Long call means buying a call option. This means the trader has the right to buy a security at a future date at a predefined price. The term long itself means buying security or buying an option. In the case of a long call, it means buying a call option.
In this detailed review, let’s try and understand the meaning of this options strategy, how it works, the corresponding formulae used for specific calculations along with knowing the pros and cons of using this options strategy.
Long Call Meaning
Options are the instruments the price of which depends on the price of the underlying asset. Options Trading is the means by which the traders have an option to buy or sell the security at a predetermined price at a predefined time in the future.
The biggest benefit of options trading is that the trader has the right but not the obligation to exercise his option. He may choose to or not to buy or sell the security, depending on whether his outlook to the market turned out correct or not.
Call option means the option to buy the security at a predetermined price called strike price at some time in the future called the expiry date.
Long Call Option Timing
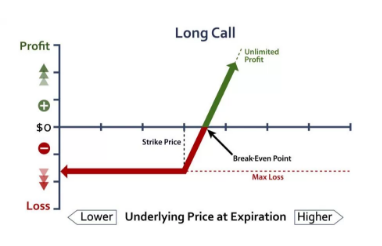
The trader enters into a contract to buy a call option when he is bullish towards the market. The trader anticipates that the price of the security will go up in the future. However, he does not want to take the risk of buying the security outright.
In this case, it is best to buy a call option on the security, which means that the trader has the rights to buy a security at a predetermined strike price at a specific date in the future.
Now, if the price of the security does go up, as anticipated by the trader, he has the rights to buy the security at the lower strike price and sell them at the higher price, thereby making profits.
However, if the price of the security does not go up, or goes down instead, the trader who is long on the call option can choose not to exercise his option.
The only loss he incurs, in this case, is of the premium that he paid for buying the call option.
Thus, by being long on a call option, the profits are unlimited, but the risks are limited only to the amount of the premium paid.
Long Call Formula
When you are using the Long Call Options strategy for your stock market trades, then you would need to calculate your profit or loss at the end of the trade.
There is a set of formula that you need to follow to objectively calculate these values.
Let’s say you make a profit in your trade, then the calculation will go like this:
Profit = Price of the Underlying Asset or Security – Premium Paid – Strike Price
With this formula, you will deduct all sort of outgoing cash from the price of the security and reach a number that you will be bagging home.
However, in case you make a loss in your trade, then the calculation will be done accordingly:
Loss = Premium + Brokerage + Taxes paid
These are pretty straight-forward calculations and can be easily calculated.
Long Call Expires In The Money
Well, this may happen but mostly, you are recommended to either roll over the contract to the next expiry date or place a “Sell To Close” order and make your profit.
However, if long call expires in the money then the call will be automatically executed and the shares in the lot will be transferred to you at the finalized strike price.
Long Call Expires Out Of The Money
If the long call option expires out of the money, then it has no value anymore.
In other words, it expires without any worth.
Well, this does happen in situations when the stock price in the market is lower than the decided strike price on the day of the long call option maturity.
Long Call Example
The long call strategy can be implemented on the shares of a particular company or on the NIFTY or Bank NIFTY.
Suppose Mahesh, a regular share market trader, is bullish for the market and anticipates that the share prices of Wipro will go up in the near future, due to an upcoming earnings release.
The shares of Wipro are currently trading at ₹256 per share and Mahesh longs a call option at the strike price of ₹280, at a premium of ₹20.
Scenario 1:
Mahesh’s anticipation comes correct and the price of Wipro’s share reaches ₹350.
Mahesh will exercise his right to buy the option and he will buy the shares at ₹280 and sell them at ₹350, making a profit of ₹70.
The net payoff will be ₹70-20 = ₹50.
Thus, the upward potential for profits is unlimited.
Scenario 2:
The price of Wipro’s share reaches ₹300. At this point Mahesh will exercise his right to buy the option and will be able to buy the share at ₹280 and sell at ₹300, making a profit of ₹20.
The net payoff will be ₹20-20 = 0.
This is the break-even point, which is equal to the strike price plus the premium.
At this price, the trader will be in a no-profit-no-loss situation.
Scenario 3:
If due to certain unforeseen circumstances, the price of shares of Wipro goes down to ₹250 per share, Mahesh has the right to not exercise his option.
In this case, he will not exercise his option and will only incur the loss of ₹20 as premium.
Thus, the loss is limited to the amount of premium paid.
It is to be noted here that in case the trader had actually bought the security instead of buying the call option, his profit could be unlimited, but at the same time, his loss potential will also be unlimited.
Thus, a long call strategy is implemented to limit the losses, by still keeping the unlimited potential for profits.
Long Call Advantages:
Here are some of the top benefits of using Long Call Option Strategy in your trades:
- This options strategy provides the potential for unlimited profits.
- The biggest advantage of a long call is that it limits the potential for losses. The maximum loss incurred can only be equal to the premium paid.
- It gives the leverage to buy the option to buy a security, instead of buying the security itself. The money required is way less.
- The long call can also be used in conjunction with the other strategies to offer flexibility to the traders in terms of income enhancement and risk reduction.
Long Call Disadvantages:
At the same time, you need to know the flip side of the coin with some of the concerns around the long call option strategy:
- The long call options are time-bound and the security price may not be able to reach the strike price by the expiry date. In this case, the option expires worthless and the trader incurs a loss equal to the amount of premium paid to buy the option.
- Leverage in long calls may affect the performance on the downside as well.
- If the investor is extremely sure of the rise in the prices, and they do, the trader will receive profit but the net payoff will be equal to the strike price minus the premium paid. If stocks were bought outright, the premium amount could have been saved.
Conclusion
If we need to summarize the whole strategy in some quick points, here is a reference for you:
Thus, we can conclude that a long call option strategy is an effective trading strategy when the trader is bullish for the market. By using long call, he can keep his profits unlimited, yet limit his losses to the amount of premium paid.
In case you are looking to trade-in options trading, well let us assist you in that. Just fill in some basic details in the form below and a callback will be arranged for you:
More on Share Market Education:
If you wish to learn more about options trading or stock market education in general, here are few references for you: