Stock Market Crash 1929
More On Share Market
Wondering what happened in the US Stock Market that leads to the biggest stock market crash in 1929?
Grab the complete information and know the facts, figures, and causes that contributed to the Great Depression period of the 1930s.
Stock Market Crash 1929 Definition
Before understanding stock market crash 1929 it is important to know a little about the Dow Jones industrial average or Dow.
Dow Jones industrial average is the stock market index that keeps track of the daily price of shares of stock of the top 30 public-owned companies of the US stock exchange.
Coming back to the US stock market crash 1929, it is the four-day collapse in the stock price during October 1929 that marked the black day in the history of the US stock market. The crash began on October 24, 1929, and ended with the biggest drop in the Dow value by 25%.
The stock market crash India of 1929 is considered to be the biggest crash in the history of the stock market. There was a sharp decline in the value of the US stock that leads to the Great Depression period.
The stock market crash of 1929 was also commonly known as the Great Crash. The severity of the crash lasted for around 10 years during which it affected both industrialized and non-industrialized countries around the globe.
Stock Market Crash 1929 Facts
The signs of the stock market crash began much before it actually took place. The good price of the stocks and the hunger to earn great profit let people ignore the warning signs which later on proved to be highly fatal for their own investment.
It was during the mid to late 1920s when the stock market underwent rapid expansion. The expansion and the stock’s high prices grab the attention of many people including banks and industrial magnates to cooks and chauffeurs. Almost every other person invested their liquid assets and securities to earn maximum profit.
In fact, people mortgaged their homes to invest maximum cash in the stock market. There were almost 300 million stock shares being carried on the margin that took the value of the Dow Jones Industrial Average to 381, the peak value of the Dow at that time.
At that time, all the warning signs went unheeded but the panic began among people when prices began to decline in September and early October.
On October 18, 1929, the market went to a free fall that continued with the generation of real panic among people on October 24, 1929. The day October 24, 1929, also known as Black Thursday was the day when investors traded around 12.9 million shares to recover their losses.
- The Dow value that opened at 305.85 dropped by 11% by the end of the day.
- The price fall increased the trading rate and finally, the market closed with a further drop in Dow by 2%.
- Although another day grew the market towards a positive direction with the increase in Dow by 1%.
- But as the market opened on October 28, 1929, marked Black Monday for investors as the Dow further fall by 13% and reached a value of 260.64.
Finally, on the fourth day October 29, 1929, the market fell by an additional 12% thus marking the Black Tuesday in the history of the US stock market. The Dow Jones Industrial Average dropped to 183 points thus closing the market at 198 on October 29. This sudden fall in the Dow by 25% led to the sale of over 16 million shares in a day.
Stock Market Crash 1929 Timeline
Get a complete overview of the cause and effect of the stock market crash 1929. The crash began much earlier but the ignorance of the warning sign resulted in a big burst in the US stock market.
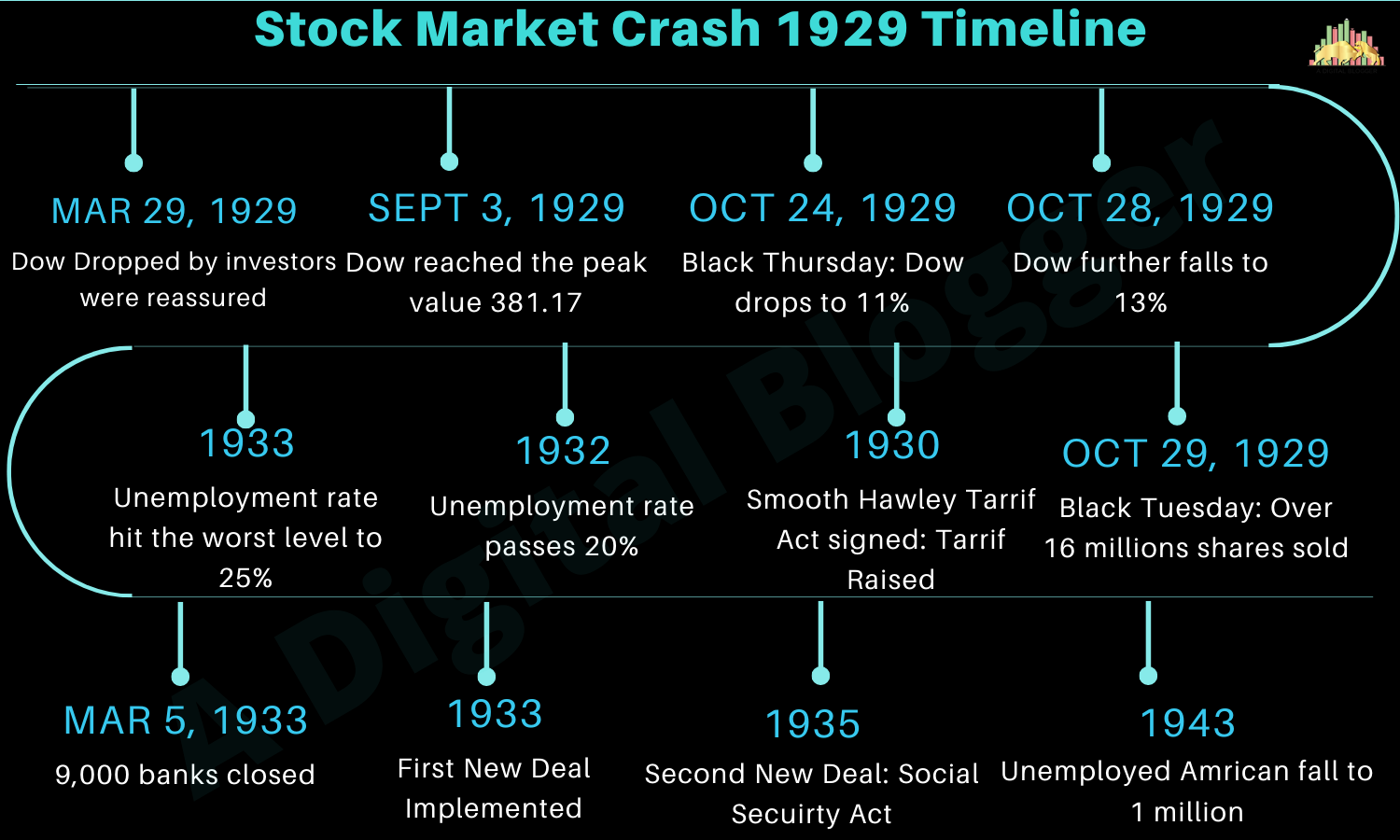
Stock Market Crash 1929 Causes
In mid to late 1929 there was an unintended rise in the inventories. This attracts the merchandisers and manufacturers. The rise led to the decline in spending and hence production which became the major cause of the Great Depression in the United States.
This decline that initiated in the US soon spread in the other parts of the world through the gold standard. Apart from these, there are many other factors that led to the downturn in the stock market and eventually the stock market crash 1929.
- Tight Monetary Policy
The tight monetary policy of the US is to limit the risks associated with the stock market.
The decade of the 1920s although the flourishing period but was not considered as the boom period. At the time the prices almost remain constant with the mild recession in 1924 and 1927.
Also, the decade marked an increase in the prices of stocks in 1921 with reaching its peak value in 1929. To control the rise in stock prices, the Federal Reserve rose the interest rates which in turn reduced the process of spending in various areas including construction and automobiles thus decreasing the production rate.
Various minor events ultimately lead to the gradual price decline of prices in October 1929 that hampers the confidence of the stock market bubble burst eventually leading to the Black day and the Great Depression period of the 1930s.
- Overconfidence Among the Market and Public
Since just before the market crash the stock prices were overpriced which did not lead the investors to believe or consider the warning signs.
Similar overconfidence was noticed among the manufacturing and agriculture industries that ultimately leads to the overproduction of a glut of items like farm crops, steel, durable goods, and iron.
The overproduction led to the cleaning out of their supplies at the loss thus affecting the share price.
This sense of overconfidence extended the average consumers and small investors thus leading to the “asset bubble”. In all, the rise in the market growth for a longer period led to the growth of overconfidence among the consumer.
- Easy Availability of Credit for Buying Stocks
During the 1920s, the rapid growth in bank credit and easy availability of loans encouraged people to take dept. Also, the prevailing concept of “buying on margin” allowed ordinary people to put the little amount of 10% of the share value and borrow the rest of the money from the stockbroker.
- Increased Interest Rates
Just before the stock market crashed in 1929, the banks increased their interest rates from 5% to 6%. This rise affected market stability thus reducing economic growth.
- Ongoing Agricultural Recession
Another major reason that contributed to the stock market crash was the agricultural recession. Farmers were struggling hard to earn the annual profit and to keep their businesses afloat. This affected the financial climate of the country to more extent.
- International Lending and Trade
According to some scholars, international lending and trade might have led to the Great Depression period and stock market crash in 1929. In the mid-1920s the foreign lending to Germany and Latin America expanded but in 1928 and 1929 the US lending abroad fell significantly because of the high-interest rate and booming stock market.
The decrease in the percentage of international lending further led to credit contraction eventually leading to further decline in the output in the foreign borrower countries.
Also Read
Stock Market Crash 1929 Charts
As per the computation, the stock market crash 1929 marked the black day in world history. Around 16,410,030 shares were traded on that day. People dumped their securities and caused downward pressure on the market. The Dow Jones was down 25% crashing the stock market.
The stock market crash 1929 is depicted by the daily, weekly, and monthly charts shown below.
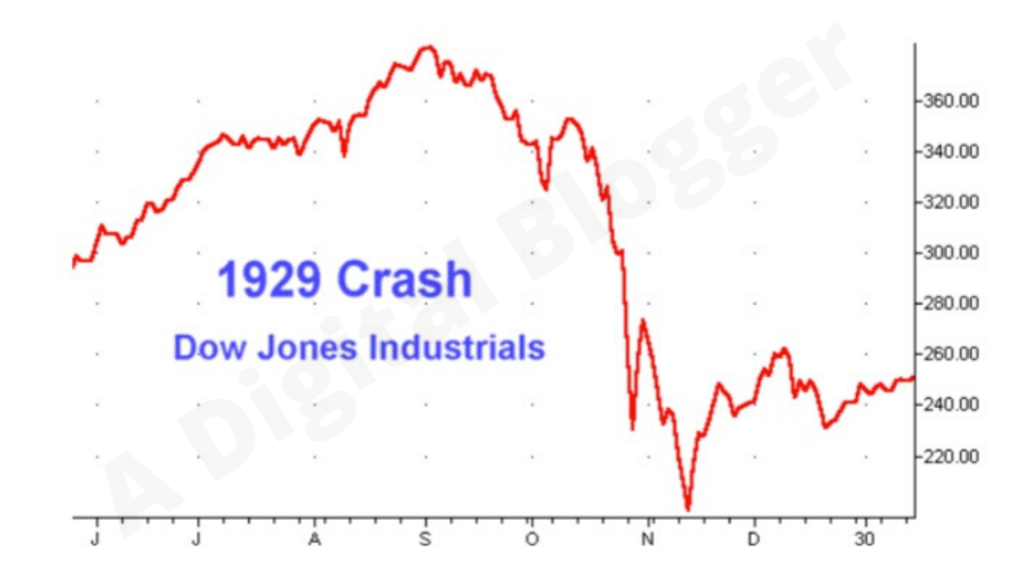
The information given in the chart above weakened when another piece of information through the chart came in front.
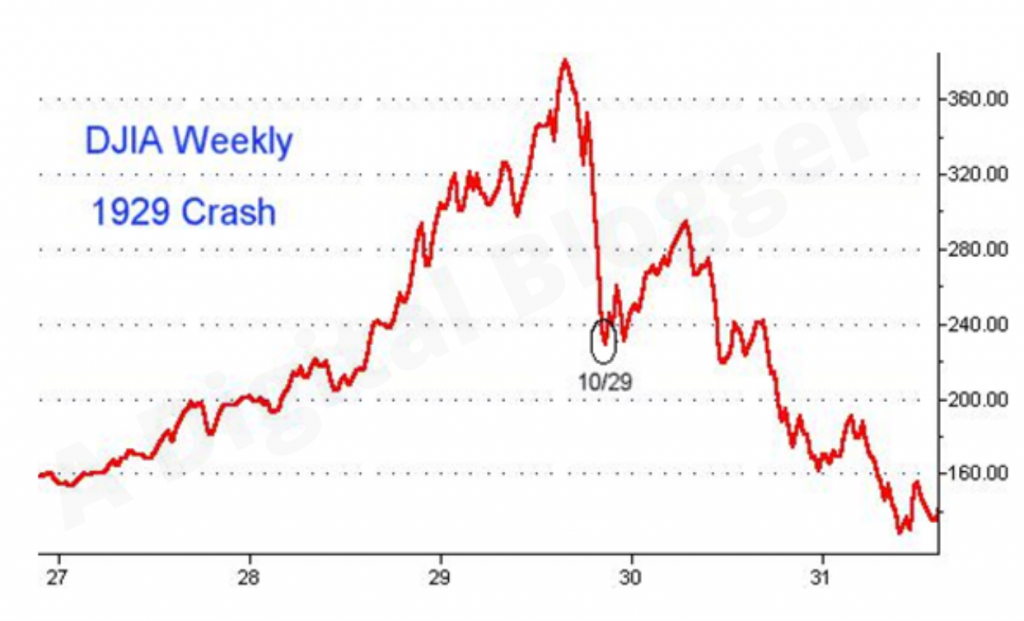
The final chart represents market status in 1932. By the time, many investors had recovered their losses with dividends, but DJIA did not come into its original form until 1954.

Stock Market Crash 1929 Effects
Since the stock market crash 1929 affected the economic state, this left the citizens of America in an awful condition for years.
On July 8, 1932, the Dow Jones fell down to 41.22. This value was almost equal to the 90% loss as compared to the highest value (381.2) recorded on September 3, 1929. After a few months on March 15, 1933, the Dow value rose to 15.34% (+8.26 points).
But overall, the stock market crash 1929 led to the fell of wages by 42%, an increased percentage of unemployment to 25%, a decrease in the U.S. economic growth, plummeted world trade by 65%.
People were having poor jobs and wages and there was no scope of savings. Also, people slowly lost their faith in Wall Street. Some other major impacts of the stock market crash 1929 were:
- Unemployment Skyrockets
It was during the period that the wages of workers were not high and the bank too was unable to offer savings for people and companies that were falling apart.
This, in turn, gives rise to the unemployment rates. Although during the initial stages the unemployment rate was under 10% which get worse in 1932 and 1933 when it reached 25%.
Although it reduces as time passed but still remains more than 10% until the US entered World War II.
- Failure of Banks
The market crash drew all the confidence and belief of the US financial system. That affected the bank severely.
The people who had their savings in the bank started withdrawing them. Since the bank did not have much cash at the time they were forced to avail loans that ultimately led to the worst scenario with the failure of more than 9,000 banks.
There was a swipe of the billions of dollars that the banks were unable to compensate.
- The defeat of the Herbert Hoover
Since the country faced major turmoil during the reign of Herbert Hoover administration thus he was easily defeated by Franklin Delano Roosevelt in the election.
Stock Market Crash 1929 Recovery
It took around 10 years for the stock market to fully recovered after the stock market crash 1929. Many theories accompanied the end of the Great Depression of the 1930s. One of them is the implementation of new policies commonly known as the New Deal when Roosevelt entered office.
- Implementation of New Deal
The recovery of the stock market crash began with the implementation of the first new deal in 1933. This deal focused on the economy, banks, and farmers. By keeping its primary focus in mind the New Deal works towards strengthening the economy and the status of the nation.
After many failures, the Emergency Bank Act was implemented that focused on stabilizing the banking system.
Along with this act, another act called the Agricultural Adjustment Act and the Emergency Farm Mortgage Act was introduced. This act aimed to save farmers, their farms and crops.
The Second New Deal began years after in 1935 intending to save businesses and industries. This New Deal focused on offering help to poor and unemployed Americans. Also, it continued to help farmers by offering them plant-specific crops.
As the National Labor Relations Act, the Second New Deal also worked towards improving the condition of workers.
The next “Third New Deal” helped in funding affordable housing and offering the overtime payment of workers.
All these programs worked together to stimulate the economy thus lowering the unemployment rate.
- World War II
Some stories behind the end of the Great Depression period of the 1930s pointed towards the beginning of World War II. During the war, Government spending went up significantly, the unemployment rate falls below 1 million unemployed Americans and there was an economic boom.
Conclusion
The stock market crash 1929 marked the Great Depression and the three key trading dates; October 24 (Thursday), October 28 (Monday), and October 29 (Tuesday).
The aberrant enthusiasm among investors during the early and mid-1920s created an unsustainable bubble that when burst collapsed the market.
The collapse not only affected the economy and affected the Dow price but also resulted in the loss of confidence among people for long. People lost their businesses overnight and many companies were bankrupt. Thus it is the worst U.S. economic crisis that ever happened in the history of the stock market.
If you are looking to know more about the Indian Share Market basics, here are some reference tutorials for you:




